Hey World welcome to drsuleinfohub.com. Anemia in pregnancy is a common nutritional disorder found during pregnancy. About 80% of maternal deaths in India are associated with Anemia. Normal Anemia is common in pregnancy but you may develop severe Anemia due to Iron deficiency or may be due to Vitamin deficiency or any other disease condition. In this article, we will see Signs and symptoms as well as the Prevention and Management of Anemia in Pregnancy.
In pregnancy Blood in your body increases by 20-30% for that you need more iron to supply Oxygen to your baby as well as your body. In pregnancy more iron is needed for the nutrition of the baby i.e. about 1000mg daily and for pregnant women daily requirement of iron is an average of 4-6 gm/day (2.5 gm/day in the first trimester, 5.5 gm/day in the second trimester, 6 to 8 gm in third trimester. WHO has accepted that 11 gm% or above is a normal level of hemoglobin in pregnancy, According to the level of hemoglobin in blood anemia in pregnancy is classified into 04 categories.
- Mild Anemia – Hb Level 09 to 11 gm%
- Moderate Anemia- Hb Level 07 to 09 gm%
- Severe Anemia Hb Level 04 to 07 gm%
- Very Severe Anemia- <04 gm%
Causes and Risk Factors
Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anemia in pregnancy. Also according to the causative factor Anemia is categorized into three causes
- Iron Deficiency Anemia
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia
- Folate Deficiency Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when the body doesn’t get enough iron for the production of hemoglobin in adequate amounts.
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia is usually found in women who don’t get enough vitamins from food. Usually, women who do not eat green leafy vegetables, fish, meat, eggs, and dairy products are at high risk of getting this type of anemia. Vitamin B12 is essential for the production of healthy red blood cells. Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia may develop neural tube defects or birth abnormalities in the fetus.
Folate deficiency anemia is caused due to a deficiency of folic acid during pregnancy. Folic acid is essential to form new cells in the body including red blood cells. Folic acid is naturally found in green leafy vegetables, and eggs naturally. Folic acid deficiency anemia also leads to neural tube defects like Spina bifida and other birth defects.
Other causes and risk factors for anemia in pregnancy include
- Multipara women (women having children more than 3)
- Two adjacent pregnancies i.e. the gap between two pregnancies is less than 1 year
- Twin babies.
- Hyperemesis gravidarum: in which a pregnant woman is having excessive nausea and vomiting in which does not get sufficient nutrition.
- A pregnant woman who has anemia before she gets pregnant due to any cause.
- Teenage pregnancy, Age less than 18 years old.
- Other underlying disease which may lead to anemia. Etc.
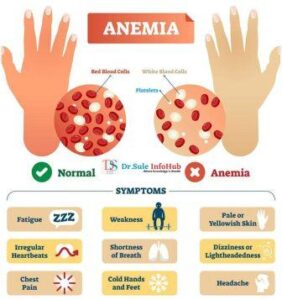
Signs and Symptoms-
When a woman is normal Anemic she does not show any major symptoms but gradually as Anemia increases she feels symptoms like,
- Generalized weakness,
- Fatigue,
- Shortness of breath,
- Breathlessness on exertion,
- Dizziness,
- Irritability,
- Palpitation,
- Vertigo,
- Digestive Upset / Indigestion.
- Foot Swelling
- Some patients may feel chest pain.
Signs of Anemia in pregnancy include
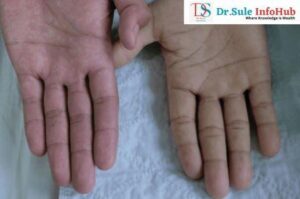
- Pallor Tongue or skin appearance,
- Tachycardia,
- Some may hear a murmur on the auscultation of the heart.
Complications of Anemia in Pregnancy
- The children of anemic mothers are at high risk of being born with iron deficiency.
- Anemia in pregnancy may lead to preterm delivery i.e. delivery of fetus before maturity.
- Post-partum hemorrhage. It is the most common cause of maternal mortality in India.
- PIH: Pregnancy-induced hypertension may develop due to Anemia.
- May give birth to Low Birth Weight babies.
- May give birth to serious birth defects like Spina Bifida, or neural tube defects.
- Babies of severe anemic women may show developmental delays in growth.
- Post-delivery complications like sepsis, depression, or convulsions.
Diagnosis / Tests for Iron deficiency Anemia.
CBC: Is the common blood test to evaluate Anemia in pregnancy is CBC or Hb estimation every month.
Low Hemoglobin or Hematocrit values are suggestive of anemia
Other tests may include:
ESR,
PBF (peripheral blood Film),
Serum Iron profile,
Bone Marrow tests
Serum Protein
Serum ferritin
Stool examination
Serum folate
RBC Folate
Serum B12
COOMBs test
Serum Electrophoresis etc. only if needed in rare cases
Home Care and Management of Anemia in Pregnancy
Once you know you are pregnant is high time to take care of yourself, To avoid anemia during
pregnancy you should take well well-balanced diet especially one rich in Iron, Folic acid, and Vitamins. This may include,
- Green leafy vegetables
- Dried beans and peas should be included in the diet.
- Eggs
- Fish and Meat
- Dry fruit like Almond seed, Dates (Kharik), Cashew nuts, and Dried Fig (Anjeer).
- Dairy products.
- Fruits rich in Vitamin C should be included in the diet, vitamin C plays an important role in the absorption of Iron in the stomach. Fruits rich in Vitamin C include Citrus fruits and their juices, Strawberries, Kiwi, Oranges, etc.
- Jeggary and Goundnut Laddoo are traditionally given to pregnant women to reduce anemia in pregnancy which is very helpful.
- Avoid calcium-rich food along with iron supplementation as Calcium can reduce iron absorption. Although Calcium is also an important nutrient during pregnancy
All girls or women should encourage routine screening from the adolescent age or before getting pregnant may reduce the risk of anemia in pregnancy.
Giving Folic Acid 5mg tablets 03 months before getting pregnant may reduce the risk of folate deficiency anemia.

Treatment and Management of Anemia in Pregnancy
If you are diagnosed with anemia, depending upon the types of anemia and severity as described above Management of anemia in pregnancy is different for different types of anemia.
If you are suffering from Iron deficiency anemia doctor will prescribe you Iron supplementation usually in the form of ferrous sulphate or ferrous ascorbate or ferrous fumarate, etc.
WHO recommends prophylactic iron supplementation of 60 mg daily for 180 days (6 Months) in pregnancy from the second trimester and 3 months after delivery is recommended.
Additional Vitamin Supplementation or Folic acid supplementation is given by doctors in Vitamin B12 and Folate deficiency anemia respectively.
Parental Iron supplementation is given to pregnant women whose Hemoglobin is below 09 gm% and not increasing on Oral Iron supplementations.
Blood Transfusion is done to a pregnant woman whose Hb level is below 07 gm% under the expert’s supervision.
Albendazole 400mg in the first or second trimester may reduce the chances of Hookworm infestation and anemia due to worm infestation.
FAQ
1) What is the main cause of anemia in pregnancy?
Ans: Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anemia in pregnancy. Also according to the causative factor Anemia is categorized into three causes.
Iron Deficiency Anemia, Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia, Folate Deficiency Anemia
2) How much anemia is normal in pregnancy?
Answer: WHO has accepted that 11 gm% or above is a normal level of hemoglobin in pregnancy, According to the level of hemoglobin in blood anemia in pregnancy is classified into 04 categories.
Mild Anemia – Hb Level 09 to 11 gm%
Moderate Anemia- Hb Level 07 to 09 gm%
Severe Anemia Hb Level 04 to 07 gm%
Very Severe Anemia- <04 gm%
3)Is anemia serious in pregnancy?
Answer: Yes, Anemia may lead to affect both on a pregnant woman as well as the fetus.
4) How the management of anemia in pregnancy is done?
Answer: Depending upon the types of anemia and severity as described above treatment is different for different types of anemia.
Oral iron supplementation
Parental iron supplementation
Blood transfusion
Vitamin supplementation
5) What food increases hemoglobin?
Answer: Green leafy vegetables, Dried beans, and peas should be included in the diet, Eggs, Fish and Meat, Dry fruit like Almond seeds, Dates (Kharik), Cashew nuts, and Dried Fig (Anjeer), Dairy products, Diet or fruits rich in Vitamin C should be included in the diet, vitamin C plays important role in the absorption of Iron in the stomach. Fruits rich in Vitamin C include Citrus fruits and their juices, Strawberries, Kiwi, Oranges, etc.
Jeggary and Goundnut Laddoo are traditionally given to pregnant women to reduce anemia in pregnancy which is very helpful.