I. Introduction of fatty liver disease
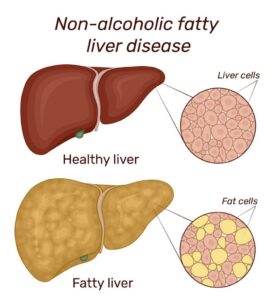
Fatty liver disease is a condition in which a large amount of fat accumulates in a person’s liver cells. It is the deposition of fat in the liver. Normally less than 5% fat cells are present in hepatocytes but if there is more than 5% fat cell in hepatocytes it will be called Fatty Liver.
Nowadays in India, fatty liver is the most common disease. Why? we will see in this article friends.
Approximately 70% people of with fatty liver remain asymptomatic they remain untreatable but some of them may develop liver fibrosis and then liver fibrosis converts into liver cirrhosis. If liver cirrhosis is left untreatable it will convert into liver cancer.
Is fatty liver dangerous? Absolutely not. How? we will see in this article.
Prevalence of the Condition of fatty liver-
The prevalence of adult NAFLD in India has been accounted for somewhere in the range of 6.7% and 55.1 % by Wikipedia.
The worldwide rate of Non-alcoholic greasy liver illness is 47 cases for each 1000 populace.
Males are more prone than females to this disease.
TYPES OF FATTY LIVER-
Fatty liver is of two types.
a) AFLD- ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
As the name mentioned this type of fatty liver disease happens due to heavy consumption of alcohol.
b) NAFLD- NON ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
This type of fatty liver disease has many reasons other than alcohol like hypertension, type 2 diabetes, increased level of triglyceride, being overweight, and overeating. Due to the above reason extra fat deposits into the liver after many years, it damages the liver and causes fatty liver disease.
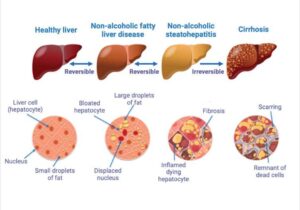
AFLD and NAFLD both have the following stages.
1) Simple fatty liver disease(hepatic steatosis)– In this condition there is deposition of fat occurs, but no inflammation.
Also in this condition, there is no harm to the liver.
2) Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)- In this condition deposition of fat occurs also there will be inflammation occurs. In this condition, damage to healthy tissue started.
3)FIBROSIS– In this condition there is deposition of more fat and inflammation present. Due to this, there is scarring happens to the liver but the liver functions normally. so the healthy tissue of the liver started to dead.
4)CIRRHOSIS – In this condition, there is much more fat deposited.
inflammation of the liver increases, scars increase, and healthy liver cells are damaged so the liver can’t function properly like bile production, digestion etc. There are fatty cells that increase and the healthy cells gradually decrease. Cirrhosis is a life-threatening health problem.
Now will see grades of fatty liver. There are grades 1,2,3 fatty liver.
Basically, this is a finding of USG to understand the severity of fatty liver.
Grade 1 fatty liver is also called mild fatty liver, grade 2 fatty liver is called moderate fatty liver, and grade 3 fatty liver is severely fatty liver.
Is fatty liver reversible? = Yes it is reversible.
Causes and Risk Factors of fatty liver diseases-
1) ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE ( AFLD) – caused by high consumption of alcohol.
2)NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE ( NAFLD) -There are many causes of NAFLD.
- Obesity is the most widely cause of NAFLD.
Greater than >22.9 BMI in Indians is a high-risk factor to develop fatty liver disease. - Uncontrolled diabetes (Type 2 diabetes mellitus.) is associated with fatty liver disease.
- Age of more than 50 years is one of the causative factors.
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Other liver infections like hepatitis B and Hepatitis C.
- In females PCOD and pregnancy.
- Steroids-Long term use of steroids causes fatty liver disease.
- Drugs like Valproate/Valproic acid used in epilepsy, seizures may cause fatty liver disease.
- Some medicines used in the treatment of cancer may cause fatty liver disease.
- Also if you lose weight rapidly within a short period increase the risk of fatty liver disease.
Signs and Symptoms of fatty liver disease.
What are the main signs of a fatty liver?
- A fatty liver is often hard to detect because its symptoms are not easily noticeable.
The first sign of fatty liver is a sharp pain and abdominal discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen. - Loss of appetite, Itchy skin, weakness, fatigue.
- Ascites- means fluid accumulation in the abdomen. This accumulation leads to abdominal pain, nausea, fullness of the abdomen, bloating, and difficulty in breathing.
- Weight loss without reason. or any try.
- Muscle atrophy, regarded as a significant complication of advanced liver disease, poses a considerable challenge to patients’ overall health.
- Jaundice- eyes become yellow and yellowish discoloration of the skin. This is due to alter function of the liver and excessive accumulation of bilirubin under the skin.
- Itchy skin, weakness, fatigue,
- Abnormal bleeding, friends, do you know which are the coagulation factors? Fibrinogen, Prothrombin, Factor V, VII, IX, X, X I as well as proteins C and S these factors responsible for coagulation. Because of fatty liver, there is decreased production of coagulation factors. So it results in easy bruising and bleeding. The nose bleeds easily.
- Spider angioma-It is a web-like cluster of blood vessels under the skin which is called spider angioma or spider telangiectasia. These growths can manifest as either multiple or solitary lesions and are typically painless.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
1. Physical Examination and Medical History
Do a physical examination for abdominal swelling or tenderness.
watch eyes, skin and nails for yellowish discoloration.
Take a history of the patient and whether he is taking any medicine like antihypertensive, anticancer etc.
2. Blood Tests and Liver Function Tests
Do CBC, and LFT.
Liver enzymes are increased in LFT.
Lipid profile -for cholesterol level.
3. Imaging Techniques
Ultrasound -By USG we will understand the grade of the liver whether it is grade-1, grade-2, or grade-3.
CT Scan, MRI
Fibroscan -by this we will understand how much liver damage is happening.
Treatment of fatty liver disease-
-Low potassium levels are associated with NAFLD prevalence so Eat potassium sources are banana, kiwi, spinach, and coconut water.
– Also you can take flaxseed as it contains anti-inflammatory properties.
Medical Treatments
-Antioxidants drugs which protect the liver from injury and reduce inflammation.
-You can take Vitamin E supplementation because Vit E is antioxidant and may be protective for the liver. Don’t take it in excessive amounts as it is fat soluble Vitamin. Take 800 units per day.
-Vitamin D deficiency may be associated with worsening the inflammation of the liver and fatty deposits. you can eat vitamin D rich diet in food.
-Vitamin B complex like pyridoxine, Vit b6. green vegetables are rich source of vit B-complex
-Fat-lowering drugs like ORLISTAT, URSODEOXYCHOLIC ACID. These medicines decrease cholesterol.
What are medications to avoid with fatty liver disease- Avoid antibiotics like erythromycin, amoxicillin, steroids, drugs used for arthritis.
Preventive Measures
1. Avoid Alcohol Intake
AFLD patients should avoid or completely stop alcohol consumption to prevent further damage.
2. Managing Diabetes and Obesity
You should control diabetes and maintain a weight normal.
3. Regular Health Check-ups
If you suffer from disease or if you have symptoms of fatty liver then go to your doctor for regular health check-ups.
Life expectancy with fatty liver disease- As liver disease is reversible after proper lifestyle modification you cure completely and live normal life.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease has no special medicine in allopathy. It can
cured by proper lifestyle management, and good diet habits.
By gaining insight into the underlying factors, identifying symptoms, and exploring available treatment choices, individuals can proactively enhance their liver health and overall state of well-being.
FAQs
What is fatty liver?
Fatty liver is a deposition of fat in liver cells.
Can fatty liver be reversed?
yes of course fatty liver disease can be reversed up to the fibrosis stage by lifestyle modification.
Fatty liver grade 1/What is grade 1 fatty liver?
Grade 1 fatty liver is a simple fatty liver disease in which a minimal amount of fat deposits in the liver. In this stage, no inflammation occurs and the liver functions normally.
How can I reduce my fatty liver disease? / Are there any specific diets for fatty liver?
Take a balanced diet like green vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
What are the long-term effects of fatty liver?
If fatty liver disease remains untreated it may convert into fibrosis after that it may lead to cirrhosis.
Does cirrhosis of the liver life-threatening?
yes! It is life-threatening. it may convert into liver cancer.